Introduction
In this article we will discuss about advantages of SRv6 technology, a dynamic force that streamlines the landscape of network protocols, catering to the evolving demands of the 5G era and the age of cloud computing. The core strengths of SRv6 are its inherent IPv6 attributes and its network programming capabilities. Leveraging the inherent IPv6 attributes, SRv6 bridges the gap between cloud and network, ensuring compatibility with existing networks and enhancing inter-AS experiences. Network programming prowess empowers SRv6 to chart optimal paths in accordance with service-level agreements and to establish intelligent cloud-network connections.
Simplifying the Network Protocol Landscape
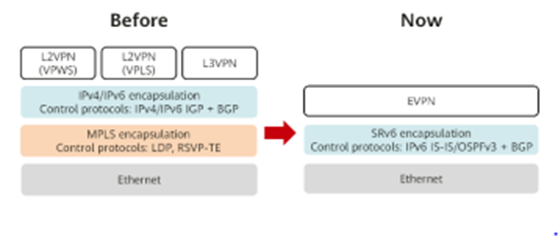
Addressing the intricacies of network evolution in the 5G and cloud era necessitates a simplified approach to IP bearer networks. SRv6 and Ethernet Virtual Private Network (EVPN) are the guiding lights in this endeavor. At the foundation, IPv6 packet extension takes over from conventional tunnel functions, rendering tunneling technologies like LDP and RSVP-TE obsolete. SRv6 introduces underlay and tunnel functions via IGP and BGP extension, thereby streamlining the signaling protocols.
On the overlay front, EVPN emerges as the unifying force, integrating L2VPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and L2VPN Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS), each rooted in LDP or MP-BGP. L3VPN, based on MP-BGP, finds its place in this orchestration. SRv6 steps onto the stage with its Segment IDs (SIDs), acting as identifiers for various services, thereby simplifying the technical complexity.
The Era of Cloud-Network Integration
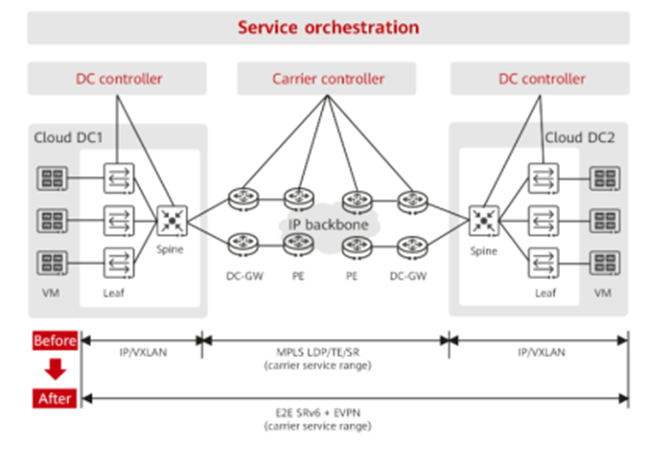
In the realm of Data Center Interconnect (DCI), where IP backbone networks use MPLS or SR-MPLS and VXLAN in the DCNs, challenges arise. Gateways enter the scene to bridge VXLAN and MPLS, adding complexities that hinder the efficiency of service deployment.
Enter SRv6 with its native IPv6 attribute. SRv6 and common IPv6 packets share the same header, allowing them to communicate seamlessly between network nodes via IPv6 reachability. This eliminates the boundaries between carrier networks and DCNs, making SRv6 a viable choice for deployment in both realms, including terminals like servers. IPv6 headers ensure communication between IPv6 nodes, while multiple IPv6 extension headers offer diverse functionalities. SRv6 capitalizes on the extensibility of IPv6, enabling simplified, end-to-end programmable networks, leading in unified service forwarding and comprehensive connectivity across the network.
Harmonizing with Existing Networks
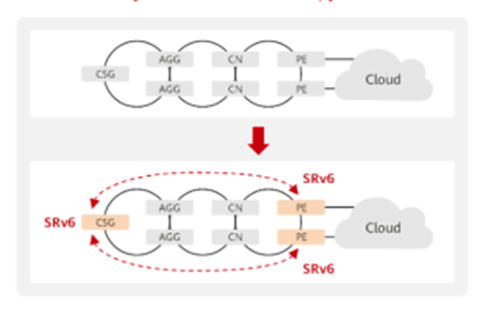
SRv6 seamlessly integrates with existing IPv6 networks, enabling swift provisioning of services on demand. The deployment of new services doesn’t demand an overhaul of the entire network, preserving existing investments. SRv6 configuration is confined to the ingress and egress points, reducing deployment time and boosting efficiency.
As depicted in below diagram, essential devices such as ingress and egress points undergo upgrades to support SRv6 in the initial phase. New services are then launched based on SRv6, with transit devices only needing IPv6 support to forward packets along IPv6 routes. Future enhancements can be made to transit nodes to provide value-added services focused on SRv6 traffic engineering.
Elevating Inter-AS Experiences
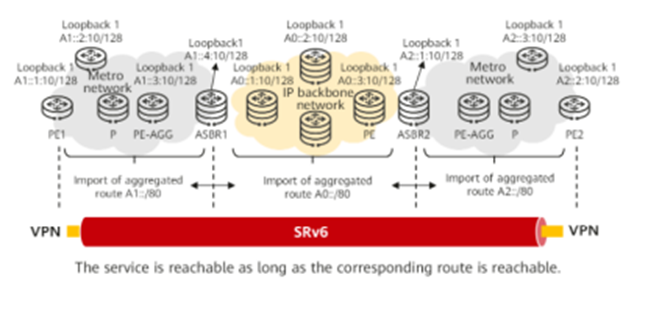
In comparison to traditional MPLS inter-AS technologies, SRv6 inter-AS deployment is more straightforward. Leveraging its native IPv6 attribute, SRv6 simplifies inter-AS service deployment by importing IPv6 routes from one AS to another using BGP4+. This simplifies service deployment and opens the doors to enhanced extensibility in inter-AS scenarios. The native IPv6 attribute empowers SRv6 to work with aggregated routes, minimizing demands on network device capabilities and enhancing network scalability.
Facilitating Agile Service Provisioning
As the landscape embraces multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud models, the demand for on-demand connections becomes paramount. Networks must provide flexible access to applications across diverse clouds while facilitating agile connections between bearer networks and clouds. This demands seamless resource scheduling and dynamic connectivity.
In traditional Layer 2 point-to-point private line setups, enterprises leased multiple site-to-cloud private lines based on cloud deployment locations. Manual adjustments or automated scheduling based on internal networking were prerequisites to access applications on different clouds, which compromised flexibility and accessibility.
The solution lies in an interconnected cloud backbone network that pre-connects multiple clouds and networks, enabling rapid cloud access upon network availability. Leveraging SRV6+ EVPN technologies, this approach facilitates adaptable connections to multiple clouds and flexible service provisioning.
In the grand symphony of technology, SRv6 stands as a conductor, orchestrating a harmonious blend of connectivity and efficiency across the digital landscape. Its unique attributes pave the way for a network realm that caters to the ever-evolving demands of the 5G and cloud era, delivering seamless communication and dynamic resource allocation across the network.
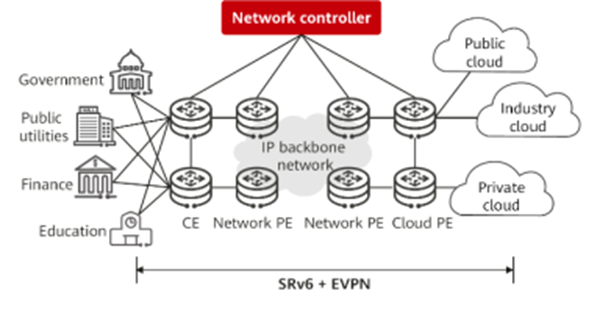
Conclusion
In the intricate landscape of networking, SRv6 technology emerges as a transformative force that redefines the way we perceive connectivity. Its native IPv6 attributes and network programming capabilities harmonize the realms of cloud and network, simplifying protocols and streamlining deployment. As the 5G era unfolds and the cloud beckons, SRv6 stands as a beacon of innovation, ushering in a new era of efficiency, scalability, and intelligent connectivity. Embracing SRv6 is embracing the future of network evolution.