Introduction
Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) is a security framework designed to enhance the reliability and security of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing system, which is fundamental to the functioning of the Internet. RPKI provides a mechanism for verifying the authenticity and validity of Internet Protocol (IP) address prefixes and Autonomous System (AS) numbers, which are essential components of routing.
RPKI systems overview
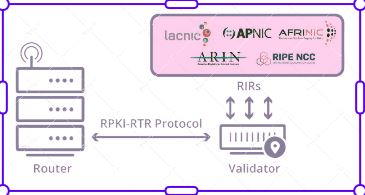
In the RPKI system, Internet Registries and Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) issue digital certificates to resource holders such as Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and organizations to verify their ownership or control over IP address blocks and AS numbers. These certificates are signed using cryptographic keys and published in a globally distributed repository called the RPKI repository.
Using RPKI, network operators can create Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) that specify valid sources of IP address prefixes and AS numbers. These ROAs are digitally signed and published in the RPKI repository along with the associated certificates. When routers receive BGP updates, they can consult the RPKI repository to verify the validity of the route announcement against the ROA
The main objective of RPKI is to prevent malicious activities such as route hijacking and IP address spoofing, which can lead to traffic interception, disruption, and security breaches. By enabling RPKI, operators can establish more secure and reliable routing infrastructure, enhancing the overall resilience and stability of the Internet.
The importance of RPKI
RPKI (Resource Public Key Infrastructure) plays a vital role in enhancing the security and trustworthiness of the Internet’s routing infrastructure. Its importance lies in several key aspects:
- Mitigating Route Hijacking: RPKI addresses the issue of route hijacking, where unauthorized entities maliciously divert or manipulate Internet traffic. By verifying the authenticity of IP address prefixes and AS numbers, RPKI enables network operators to detect and prevent illegitimate route announcements, reducing the risk of route hijacking incidents.
- Preventing IP Address Spoofing: IP address spoofing involves forging the source IP address in network packets, making it difficult to trace the origin of malicious activities. RPKI helps prevent IP address spoofing by ensuring that IP address prefixes are legitimately assigned to the announcing entities. This verification enables better identification and prevention of spoofed traffic.
- Enhancing Network Security: By providing a mechanism to validate the origin of IP address prefixes and AS numbers, RPKI strengthens the overall security of Internet routing. It helps protect against unauthorized route injections, route leaks, and the propagation of incorrect routing information. With improved security, the risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, and traffic interception are significantly reduced.
- Increasing Routing Efficiency: RPKI facilitates more efficient and reliable routing operations. By ensuring that routing announcements are legitimate and authorized, network operators can make informed decisions about the paths they select for traffic. This enhances the accuracy and efficiency of routing, minimizing unnecessary traffic congestion and improving overall network performance.
- Fostering Trust and Collaboration: RPKI promotes trust among network operators, service providers, and organizations by establishing a standardized framework for verifying routing information. It encourages collaboration between entities to collectively enhance the security and reliability of the Internet’s routing system. RPKI also enables the development of new security features and protocols that build upon its foundation.
The Basics of BGP Routing
BGP is a critical protocol that enables the exchange of routing information between ASes, forming the backbone of the Internet’s inter-domain routing. It relies on path attributes, route selection mechanisms, and policies to determine the best routes and ensure the efficient and reliable delivery of network traffic across AS boundaries.
BGP security weaknesses
BGP has some common security weakness. Some of them are described below:
- Lack of Authentication: BGP does not inherently provide strong authentication mechanisms, making it vulnerable to attacks like route hijacking and unauthorized route advertisement. Without proper authentication, malicious entities can impersonate legitimate routers or inject false routing information.
- Lack of Integrity Protection: BGP does not include built-in mechanisms to ensure the integrity of routing updates. This leaves the protocol susceptible to tampering, where attackers can modify or inject false routing information, leading to disruptions or unauthorized routing paths.
- Insufficient Route Validation: BGP relies heavily on the information received from neighbouring routers. If these updates are not properly validated, incorrect or malicious routing information can propagate throughout the network, leading to suboptimal routing, congestion, or service disruptions.
- Limited Confidentiality: BGP updates are exchanged in plaintext, making them liable to eavesdropping and unauthorized access. This lack of confidentiality can expose sensitive network information, including routing decisions, network topology, and potential points of attack.
- BGP Misconfigurations: Human errors and misconfigurations in BGP routers can introduce vulnerabilities. These misconfigurations can result in unintended route leaks, incorrect routing information propagation, or incorrect filtering, potentially leading to security incidents or service disruptions.
- Lack of Real-time Monitoring: BGP lacks effective real-time monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. This makes it challenging to identify and mitigate attacks, such as route hijacking or unauthorized route advertisement, in a timely manner.
- Dependency on Trust: BGP relies heavily on trust relationships between ASes. However, trust can be exploited, and compromised relationships can lead to malicious activities, unauthorized routing changes, or the propagation of incorrect routing information.
Addressing these security weaknesses requires the adoption of additional security measures, such as secure BGP extensions (S-BGP), BGPsec, route origin validation (ROV) using Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI), secure BGP peering, and implementing robust configuration and monitoring practices to enhance the overall security and resilience of the BGP routing system.
The Role of RPKI in BGP Routing Security
The Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) plays a crucial role in enhancing the security of BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) routing. Here’s a brief description of the role of RPKI in BGP routing security:
- Route Origin Validation: RPKI provides a mechanism for validating the origin of BGP routing information. It allows network operators to digitally sign their IP address prefixes and Autonomous System (AS) numbers with cryptographic certificates. These signed objects, known as Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs), indicate the legitimate origin of the routing information.
- Preventing Route Hijacking: By leveraging RPKI, BGP routers can verify the authenticity of routing updates received from neighbouring routers. They cross-reference the received routing information with the ROAs stored in the RPKI repository to determine whether the routes are authorized. This helps to prevent route hijacking, where malicious entities try to divert or manipulate traffic by announcing unauthorized routes.
- Mitigating IP Address Spoofing: RPKI helps in mitigating IP address spoofing attacks. By validating the legitimacy of IP address prefixes, RPKI helps ensure that routers only accept routing information originating from authorized entities. This prevents the propagation of spoofed IP addresses and enhances the overall security of BGP routing.
- Improving Trust and Confidence: RPKI enhances trust and confidence in the BGP routing system by providing a standardized framework for verifying routing information. It enables network operators to make informed decisions based on validated route origins, reducing the risk of inadvertently accepting unauthorized or incorrect routing updates.
- Supporting Route Filtering: RPKI enables more effective and granular route filtering. Network operators can use the ROAs to specify their intended route advertisements and validate incoming routes based on these assertions. This helps prevent the propagation of invalid or unauthorized routes, leading to more accurate and secure routing decisions.
- Enhancing Internet Routing Security: By addressing vulnerabilities in BGP routing, RPKI enhances the overall security and stability of the Internet. It provides a framework to mitigate risks associated with route hijacking, IP address spoofing, and the propagation of incorrect routing information. RPKI’s adoption contributes to a more resilient and trustworthy Internet routing infrastructure.
To continue reading related to RPKI, checkout below post:
RPKI solutions for BGP route hijacking